二叉堆 Binary Heap
https://labuladong.github.io/algo/2/20/52/
二叉堆(Binary Heap)没什么神秘,性质比二叉搜索树 BST 还简单。其主要操作就两个,sink(下沉)和 swim(上浮),用以维护二叉堆的性质。其主要应用有两个,首先是一种排序方法「堆排序」,第二是一种很有用的数据结构「优先级队列」。
本文就以实现优先级队列(Priority Queue)为例,来讲讲一下二叉堆怎么运作的。
一、二叉堆概览
首先,二叉堆和二叉树有啥关系呢,为什么人们总是把二叉堆画成一棵二叉树?
因为,二叉堆在逻辑上其实是一种特殊的二叉树(完全二叉树),只不过存储在数组里。一般的链表二叉树,我们操作节点的指针,而在数组里,我们把数组索引作为指针:
// 父节点的索引
int parent(int root) {
return root / 2;
}
// 左孩子的索引
int left(int root) {
return root * 2;
}
// 右孩子的索引
int right(int root) {
return root * 2 + 1;
}画个图你立即就能理解了,比如 arr 是一个字符数组,注意数组的第一个索引 0 空着不用:
你看到了,因为这棵二叉树是「完全二叉树」,所以把 arr[1] 作为整棵树的根的话,每个节点的父节点和左右孩子的索引都可以通过简单的运算得到,这就是二叉堆设计的一个巧妙之处。
为了方便讲解,下面都会画的图都是二叉树结构,相信你能把树和数组对应起来。
二叉堆还分为最大堆和最小堆。最大堆的性质是:每个节点都大于等于它的两个子节点。类似的,最小堆的性质是:每个节点都小于等于它的子节点。
两种堆核心思路都是一样的,本文以最大堆为例讲解。
对于一个最大堆,根据其性质,显然堆顶,也就是 arr[1] 一定是所有元素中最大的元素。
二、优先级队列概览
优先级队列这种数据结构有一个很有用的功能,你插入或者删除元素的时候,元素会自动排序,这底层的原理就是二叉堆的操作。
数据结构的功能无非增删查该,优先级队列有两个主要 API,分别是 insert 插入一个元素和 delMax 删除最大元素(如果底层用最小堆,那么就是 delMin)。
下面我们实现一个简化的优先级队列,先看下代码框架:
PS:这里用到 Java 的泛型,
Key可以是任何一种可比较大小的数据类型,比如 Integer 等类型。
空出来的四个方法是二叉堆和优先级队列的奥妙所在,下面用图文来逐个理解。
三、实现 swim 和 sink
为什么要有上浮 swim 和下沉 sink 的操作呢?为了维护堆结构。
我们要讲的是最大堆,每个节点都比它的两个子节点大,但是在插入元素和删除元素时,难免破坏堆的性质,这就需要通过这两个操作来恢复堆的性质了。
对于最大堆,会破坏堆性质的有两种情况:
如果某个节点 A 比它的子节点(中的一个)小,那么 A 就不配做父节点,应该下去,下面那个更大的节点上来做父节点,这就是对 A 进行下沉。
如果某个节点 A 比它的父节点大,那么 A 不应该做子节点,应该把父节点换下来,自己去做父节点,这就是对 A 的上浮。
当然,错位的节点 A 可能要上浮(或下沉)很多次,才能到达正确的位置,恢复堆的性质。所以代码中肯定有一个 while 循环。
细心的读者也许会问,这两个操作不是互逆吗,所以上浮的操作一定能用下沉来完成,为什么我还要费劲写两个方法?
是的,操作是互逆等价的,但是最终我们的操作只会在堆底和堆顶进行(等会讲原因),显然堆底的「错位」元素需要上浮,堆顶的「错位」元素需要下沉。
上浮的代码实现:
画个 GIF 看一眼就明白了:
下沉的代码实现:
下沉比上浮略微复杂一点,因为上浮某个节点 A,只需要 A 和其父节点比较大小即可;但是下沉某个节点 A,需要 A 和其两个子节点比较大小,如果 A 不是最大的就需要调整位置,要把较大的那个子节点和 A 交换。
画个 GIF 看下就明白了:
至此,二叉堆的主要操作就讲完了,一点都不难吧,代码加起来也就十行。明白了 sink 和 swim 的行为,下面就可以实现优先级队列了。
四、实现 delMax 和 insert
这两个方法就是建立在 swim 和 sink 上的。
insert 方法先把要插入的元素添加到堆底的最后,然后让其上浮到正确位置。
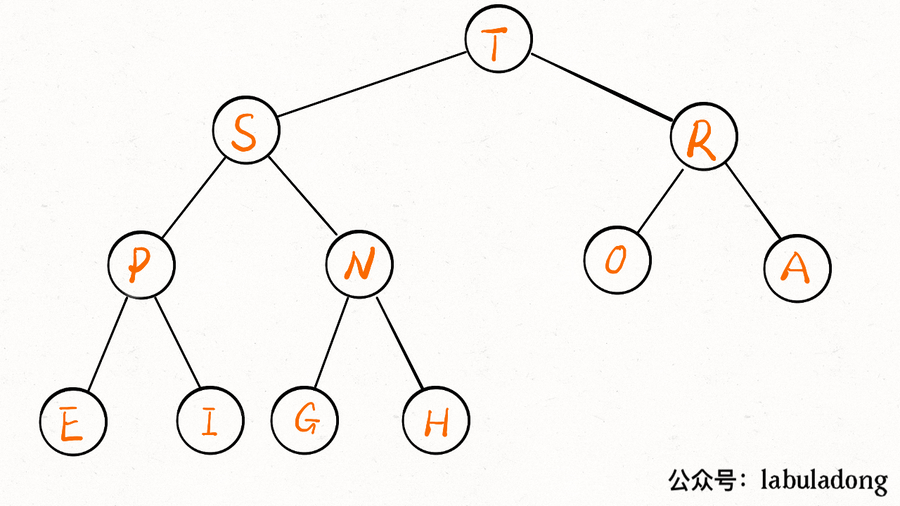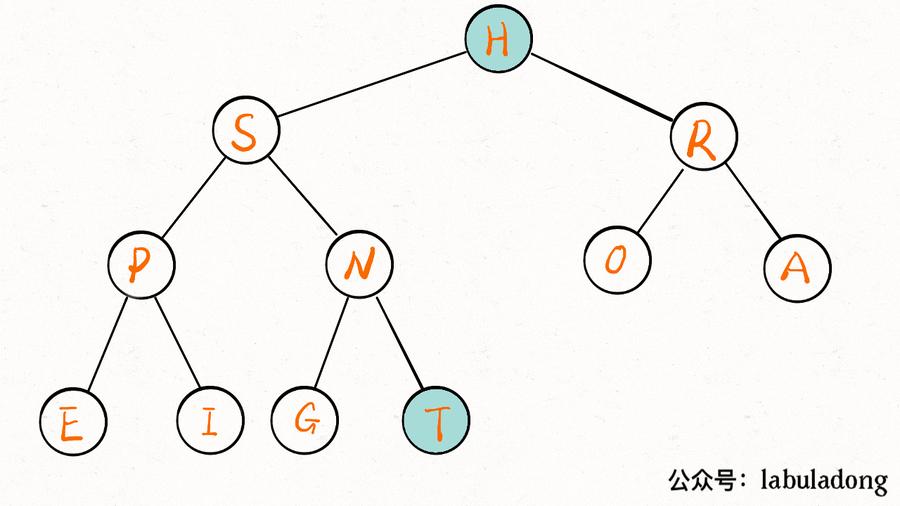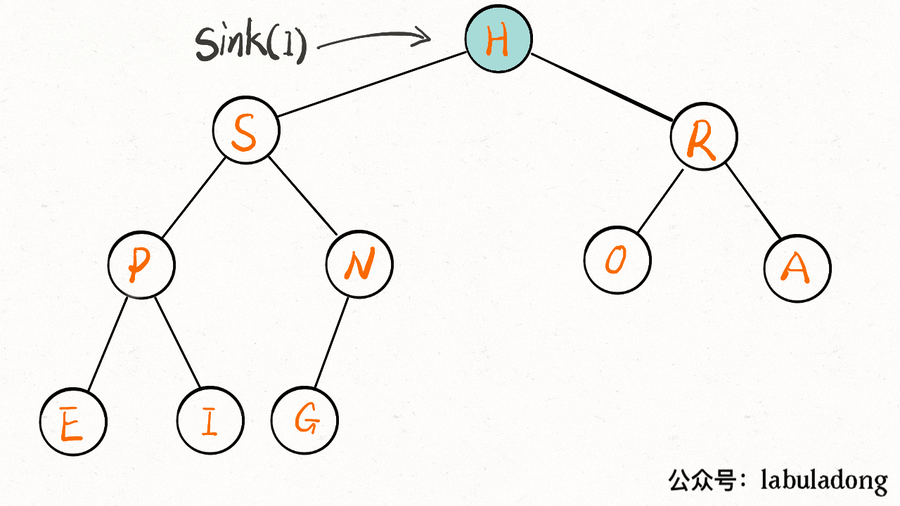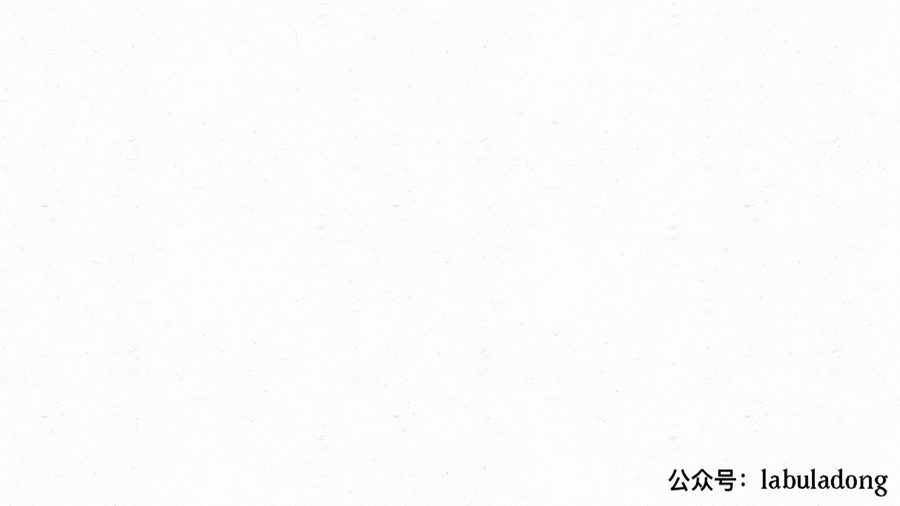
delMax 方法先把堆顶元素 A 和堆底最后的元素 B 对调,然后删除 A,最后让 B 下沉到正确位置。
至此,一个优先级队列就实现了,插入和删除元素的时间复杂度为 O(logK),K 为当前二叉堆(优先级队列)中的元素总数。因为我们时间复杂度主要花费在 sink 或者 swim 上,而不管上浮还是下沉,最多也就树(堆)的高度,也就是 log 级别。
五、最后总结
二叉堆就是一种完全二叉树,所以适合存储在数组中,而且二叉堆拥有一些特殊性质。
二叉堆的操作很简单,主要就是上浮和下沉,来维护堆的性质(堆有序),核心代码也就十行。
优先级队列是基于二叉堆实现的,主要操作是插入和删除。插入是先插到最后,然后上浮到正确位置;删除是调换位置后再删除,然后下沉到正确位置。核心代码也就十行。
也许这就是数据结构的威力,简单的操作就能实现巧妙的功能,真心佩服发明二叉堆算法的人!
六.Heap Sort 原理
http://www.itdadao.com/articles/c15a1041906p0.html
http://bubkoo.com/2014/01/14/sort-algorithm/heap-sort/
堆排序就是把最大堆堆顶的最大数取出,将剩余的堆继续调整为最大堆,再次将堆顶的最大数取出,这个过程持续到剩余数只有一个时结束。在堆中定义以下几种操作:
最大堆调整(Max-Heapify):将堆的末端子节点作调整,使得子节点永远小于父节点
创建最大堆(Build-Max-Heap):将堆所有数据重新排序,使其成为最大堆
堆排序(Heap-Sort):移除位在第一个数据的根节点,并做最大堆调整的递归运算
最大堆调整(MAX‐HEAPIFY)的作用是保持最大堆的性质,是创建最大堆的核心子程序,

创建最大堆(Build-Max-Heap)的作用是将一个数组改造成一个最大堆,接受数组和堆大小两个参数,Build-Max-Heap 将自下而上的调用 Max-Heapify 来改造数组,建立最大堆。
因为 Max-Heapify 能够保证下标 i 的结点之后结点都满足最大堆的性质,所以自下而上的调用 Max-Heapify 能够在改造过程中保持这一性质。如果最大堆的数量元素是 n,那么 Build-Max-Heap 从 Parent(n) 开始,往上依次调用 Max-Heapify。流程如下:

堆排序(Heap-Sort)是堆排序的接口算法,Heap-Sort先调用Build-Max-Heap将数组改造为最大堆,然后将堆顶和堆底元素交换,之后将底部上升,最后重新调用Max-Heapify保持最大堆性质。由于堆顶元素必然是堆中最大的元素,所以一次操作之后,堆中存在的最大元素被分离出堆,重复n-1次之后,数组排列完毕。整个流程如下:

Last updated