95. Unique Binary Search Trees II (M)
https://leetcode.com/problems/unique-binary-search-trees-ii/
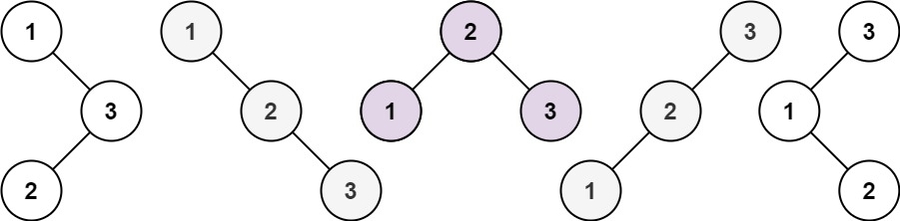
Input: n = 3
Output: [[1,null,2,null,3],[1,null,3,2],[2,1,3],[3,1,null,null,2],[3,2,null,1]]Input: n = 1
Output: [[1]]Solution:
代码思路
复杂度分析
源代码
Last updated