931. Minimum Falling Path Sum (M)
https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-falling-path-sum/
Given an n x n array of integers matrix, return the minimum sum of any falling path through matrix.
A falling path starts at any element in the first row and chooses the element in the next row that is either directly below or diagonally left/right. Specifically, the next element from position (row, col) will be (row + 1, col - 1), (row + 1, col), or (row + 1, col + 1).
Example 1:
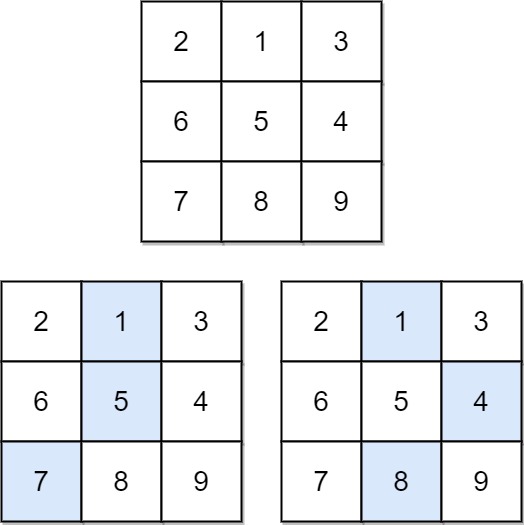
Input: matrix = [[2,1,3],[6,5,4],[7,8,9]]
Output: 13
Explanation: There are two falling paths with a minimum sum as shown.Example 2:
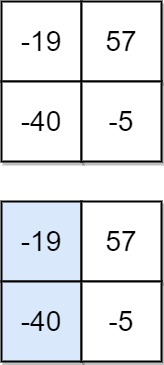
Input: matrix = [[-19,57],[-40,-5]]
Output: -59
Explanation: The falling path with a minimum sum is shown.
Constraints:
n == matrix.length == matrix[i].length1 <= n <= 100-100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100
Solution:
今天这道题也是类似的,不算是困难的题目,所以我们借这道题来讲讲 base case 的返回值、备忘录的初始值、索引越界情况的返回值如何确定。
不过还是要通过 动态规划的标准套路 介绍一下这道题的解题思路,首先我们可以定义一个 dp 数组:
这个 dp 函数的含义如下:
从第一行(matrix[0][..])向下落,落到位置 matrix[i][j] 的最小路径和为 dp(matrix, i, j)。
根据这个定义,我们可以把主函数的逻辑写出来:
因为我们可能落到最后一行的任意一列,所以要穷举一下,看看落到哪一列才能得到最小的路径和。
接下来看看 dp 函数如何实现。
对于 matrix[i][j],只有可能从 matrix[i-1][j], matrix[i-1][j-1], matrix[i-1][j+1] 这三个位置转移过来。
那么,只要知道到达 (i-1, j), (i-1, j-1), (i-1, j+1) 这三个位置的最小路径和,加上 matrix[i][j] 的值,就能够计算出来到达位置 (i, j) 的最小路径和:
当然,上述代码是暴力穷举解法,我们可以用备忘录的方法消除重叠子问题,完整代码如下:
如果看过我们公众号之前的动态规划系列文章,这个解题思路应该是非常容易理解的。
那么本文对于这个 dp 函数仔细探讨三个问题:
1、对于索引的合法性检测,返回值为什么是 99999?其他的值行不行?
2、base case 为什么是 i == 0?
3、备忘录 memo 的初始值为什么是 66666?其他值行不行?
首先,说说 base case 为什么是 i == 0,返回值为什么是 matrix[0][j],这是根据 dp 函数的定义所决定的。
回顾我们的 dp 函数定义:
从第一行(matrix[0][..])向下落,落到位置 matrix[i][j] 的最小路径和为 dp(matrix, i, j)。
根据这个定义,我们就是从 matrix[0][j] 开始下落。那如果我们想落到的目的地就是 i == 0,所需的路径和当然就是 matrix[0][j] 呗。
再说说备忘录 memo 的初始值为什么是 66666,这是由题目给出的数据范围决定的。
备忘录 memo 数组的作用是什么?
就是防止重复计算,将 dp(matrix, i, j) 的计算结果存进 memo[i][j],遇到重复计算可以直接返回。
那么,我们必须要知道 memo[i][j] 到底存储计算结果没有,对吧?如果存结果了,就直接返回;没存,就去递归计算。
所以,memo 的初始值一定得是特殊值,和合法的答案有所区分。
我们回过头看看题目给出的数据范围:
matrix是n x n的二维数组,其中1 <= n <= 100;对于二维数组中的元素,有-100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100。
假设 matrix 的大小是 100 x 100,所有元素都是 100,那么从第一行往下落,得到的路径和就是 100 x 100 = 10000,也就是最大的合法答案。
类似的,依然假设 matrix 的大小是 100 x 100,所有元素是 -100,那么从第一行往下落,就得到了最小的合法答案 -100 x 100 = -10000。
也就是说,这个问题的合法结果会落在区间 [-10000, 10000] 中。
所以,我们 memo 的初始值就要避开区间 [-10000, 10000],换句话说,memo 的初始值只要在区间 (-inf, -10001] U [10001, +inf) 中就可以。
最后,说说对于不合法的索引,返回值应该如何确定,这需要根据我们状态转移方程的逻辑确定。
对于这道题,状态转移的基本逻辑如下:
显然,i - 1, j - 1, j + 1 这几个运算可能会造成索引越界,对于索引越界的 dp 函数,应该返回一个不可能被取到的值。
因为我们调用的是 min 函数,最终返回的值是最小值,所以对于不合法的索引,只要 dp 函数返回一个永远不会被取到的最大值即可。
刚才说了,合法答案的区间是 [-10000, 10000],所以我们的返回值只要大于 10000 就相当于一个永不会取到的最大值。
换句话说,只要返回区间 [10001, +inf) 中的一个值,就能保证不会被取到。
至此,我们就把动态规划相关的三个细节问题举例说明了。
拓展延伸一下,建议大家做题时,除了题意本身,一定不要忽视题目给定的其他信息。
本文举的例子,测试用例数据范围可以确定「什么是特殊值」,从而帮助我们将思路转化成代码。
除此之外,数据范围还可以帮我们估算算法的时间/空间复杂度。
比如说,有的算法题,你只想到一个暴力求解思路,时间复杂度比较高。如果发现题目给定的数据量比较大,那么肯定可以说明这个求解思路有问题或者存在优化的空间。
除了数据范围,有时候题目还会限制我们算法的时间复杂度,这种信息其实也暗示着一些东西。
比如要求我们的算法复杂度是 O(NlogN),你想想怎么才能搞出一个对数级别的复杂度呢?
肯定得用到 二分搜索 或者二叉树相关的数据结构,比如 TreeMap,PriorityQueue 之类的对吧。
再比如,有时候题目要求你的算法时间复杂度是 O(MN),这可以联想到什么?
可以大胆猜测,常规解法是用 回溯算法 暴力穷举,但是更好的解法是动态规划,而且是一个二维动态规划,需要一个 M * N 的二维 dp 数组,所以产生了这样一个时间复杂度。
如果你早就胸有成竹了,那就当我没说,毕竟猜测也不一定准确;但如果你本来就没啥解题思路,那有了这些推测之后,最起码可以给你的思路一些方向吧?
总之,多动脑筋,不放过任何蛛丝马迹,你不成为刷题小能手才怪。
Last updated
