四键键盘问题很有意思,而且可以明显感受到:对 dp 数组的不同定义需要完全不同的逻辑,从而产生完全不同的解法。
首先看一下题目:
如何在 N 次敲击按钮后得到最多的 A?我们穷举呗,每次有对于每次按键,我们可以穷举四种可能,很明显就是一个动态规划问题。
这种思路会很容易理解,但是效率并不高,我们直接走流程:对于动态规划问题,首先要明白有哪些「状态」,有哪些「选择」。
具体到这个问题,对于每次敲击按键,有哪些「选择」是很明显的:4 种,就是题目中提到的四个按键,分别是 A、C-A、C-C、C-V(Ctrl 简写为 C)。
接下来,思考一下对于这个问题有哪些「状态」?或者换句话说,我们需要知道什么信息,才能将原问题分解为规模更小的子问题?
你看我这样定义三个状态行不行:第一个状态是剩余的按键次数,用 n 表示;第二个状态是当前屏幕上字符 A 的数量,用 a_num 表示;第三个状态是剪切板中字符 A 的数量,用 copy 表示。
如此定义「状态」,就可以知道 base case:当剩余次数 n 为 0 时,a_num 就是我们想要的答案。
结合刚才说的 4 种「选择」,我们可以把这几种选择通过状态转移表示出来:
dp(n - 1, a_num + 1, copy), # A
解释:按下 A 键,屏幕上加一个字符
同时消耗 1 个操作数
dp(n - 1, a_num + copy, copy), # C-V
解释:按下 C-V 粘贴,剪切板中的字符加入屏幕
同时消耗 1 个操作数
dp(n - 2, a_num, a_num) # C-A C-C
解释:全选和复制必然是联合使用的,
剪切板中 A 的数量变为屏幕上 A 的数量
同时消耗 2 个操作数
这样可以看到问题的规模 n 在不断减小,肯定可以到达 n = 0 的 base case,所以这个思路是正确的:
这个解法应该很好理解,因为语义明确。下面就继续走流程,用备忘录消除一下重叠子问题:
这样优化代码之后,子问题虽然没有重复了,但数目仍然很多,在 LeetCode 提交会超时的。
我们尝试分析一下这个算法的时间复杂度,就会发现不容易分析。我们可以把这个 dp 函数写成 dp 数组:
我们知道变量 n 最多为 N,但是 a_num 和 copy 最多为多少我们很难计算,复杂度起码也有 O(N^3) 把。所以这个算法并不好,复杂度太高,且已经无法优化了。
这也就说明,我们这样定义「状态」是不太优秀的,下面我们换一种定义 dp 的思路。
这种思路稍微有点复杂,但是效率高。继续走流程,「选择」还是那 4 个,但是这次我们只定义一个「状态」,也就是剩余的敲击次数 n。
这个算法基于这样一个事实,最优按键序列一定只有两种情况:
要么一直按 A:A,A,…A(当 N 比较小时)。
要么是这么一个形式:A,A,…C-A,C-C,C-V,C-V,…C-V(当 N 比较大时)。
因为字符数量少(N 比较小)时,C-A C-C C-V 这一套操作的代价相对比较高,可能不如一个个按 A;而当 N 比较大时,后期 C-V 的收获肯定很大。这种情况下整个操作序列大致是:开头连按几个 A,然后 C-A C-C 组合再接若干 C-V,然后再 C-A C-C 接着若干 C-V,循环下去。
换句话说,最后一次按键要么是 A 要么是 C-V。明确了这一点,可以通过这两种情况来设计算法:
对于「按 A 键」这种情况,就是状态 i - 1 的屏幕上新增了一个 A 而已,很容易得到结果:
但是,如果要按 C-V,还要考虑之前是在哪里 C-A C-C 的。
刚才说了,最优的操作序列一定是 C-A C-C 接着若干 C-V,所以我们用一个变量 j 作为若干 C-V 的起点。那么 j 之前的 2 个操作就应该是 C-A C-C 了:
其中 j 变量减 2 是给 C-A C-C 留下操作数,看个图就明白了:
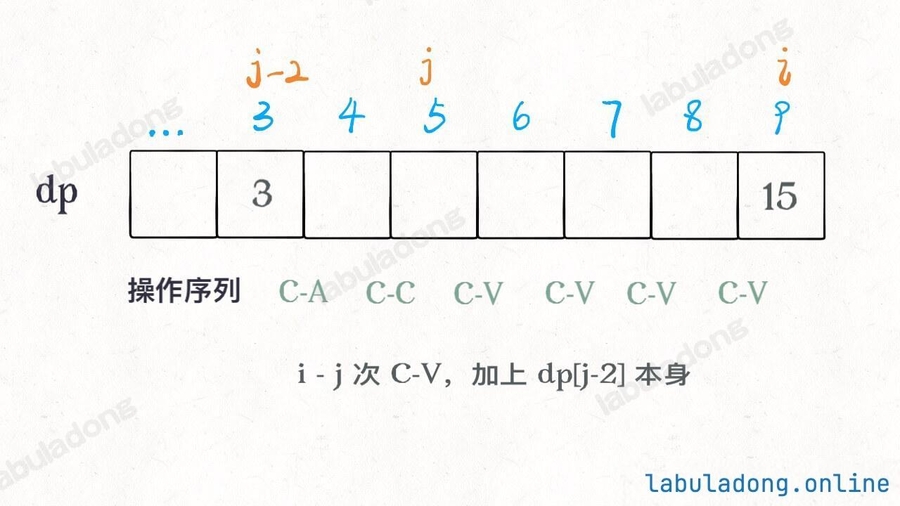
这样,此算法就完成了,时间复杂度 O(N^2),空间复杂度 O(N),这种解法应该是比较高效的了。
动态规划难就难在寻找状态转移,不同的定义可以产生不同的状态转移逻辑,虽然最后都能得到正确的结果,但是效率可能有巨大的差异。
回顾第一种解法,重叠子问题已经消除了,但是效率还是低,到底低在哪里呢?抽象出递归框架:
看这个穷举逻辑,是有可能出现这样的操作序列 C-A C-C,C-A C-C... 或者 C-V,C-V,...。然这种操作序列的结果不是最优的,但是我们并没有想办法规避这些情况的发生,从而增加了很多没必要的子问题计算。
回顾第二种解法,我们稍加思考就能想到,最优的序列应该是这种形式:A,A..C-A,C-C,C-V,C-V..C-A,C-C,C-V..。
根据这个事实,我们重新定义了状态,重新寻找了状态转移,从逻辑上减少了无效的子问题个数,从而提高了算法的效率。

