Trie Application
Summary
This article is for intermediate level users. It introduces the following ideas: The data structure Trie (Prefix tree) and most common operations with it.
Solution
Applications
Trie (we pronounce "try") or prefix tree is a tree data structure, which is used for retrieval of a key in a dataset of strings. There are various applications of this very efficient data structure such as :
1. Autocomplete
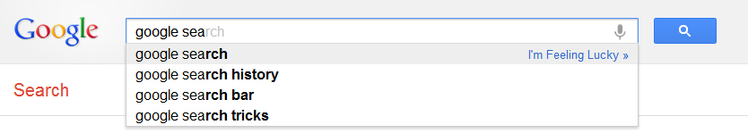
Figure 1. Google Suggest in action.
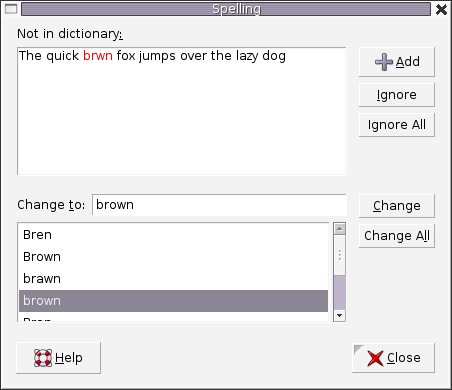
Figure 2. A spell checker used in word processor.
3. IP routing (Longest prefix matching)
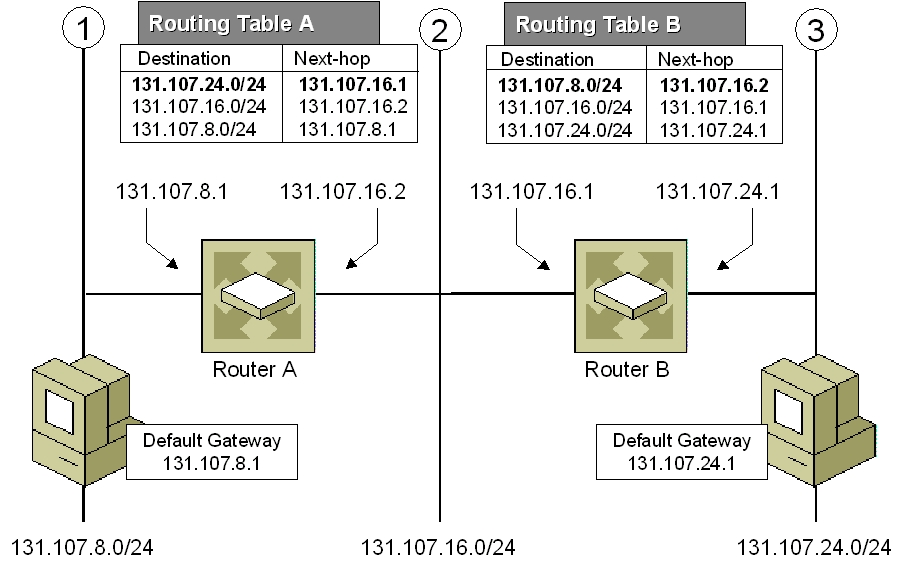
Figure 3. Longest prefix matching algorithm uses Tries in Internet Protocol (IP) routing to select an entry from a forwarding table.
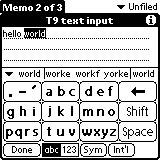
Figure 4. T9 which stands for Text on 9 keys, was used on phones to input texts during the late 1990s.

Figure 5. Tries is used to solve Boggle efficiently by pruning the search space.
There are several other data structures, like balanced trees and hash tables, which give us the possibility to search for a word in a dataset of strings. Then why do we need trie? Although hash table has O(1)O(1) time complexity for looking for a key, it is not efficient in the following operations :
Finding all keys with a common prefix.
Enumerating a dataset of strings in lexicographical order.
Another reason why trie outperforms hash table, is that as hash table increases in size, there are lots of hash collisions and the search time complexity could deteriorate to O(n)O(n), where nn is the number of keys inserted. Trie could use less space compared to Hash Table when storing many keys with the same prefix. In this case using trie has only O(m)O(m) time complexity, where mm is the key length. Searching for a key in a balanced tree costs O(m \log n)O(mlogn) time complexity.
Trie node structure
Trie is a rooted tree. Its nodes have the following fields:
Maximum of RR links to its children, where each link corresponds to one of RR character values from dataset alphabet. In this article we assume that RR is 26, the number of lowercase latin letters.
Boolean field which specifies whether the node corresponds to the end of the key, or is just a key prefix.

Figure 6. Representation of a key "leet" in trie.
Java
Two of the most common operations in a trie are insertion of a key and search for a key.
Insertion of a key to a trie
We insert a key by searching into the trie. We start from the root and search a link, which corresponds to the first key character. There are two cases :
A link exists. Then we move down the tree following the link to the next child level. The algorithm continues with searching for the next key character.
A link does not exist. Then we create a new node and link it with the parent's link matching the current key character. We repeat this step until we encounter the last character of the key, then we mark the current node as an end node and the algorithm finishes.
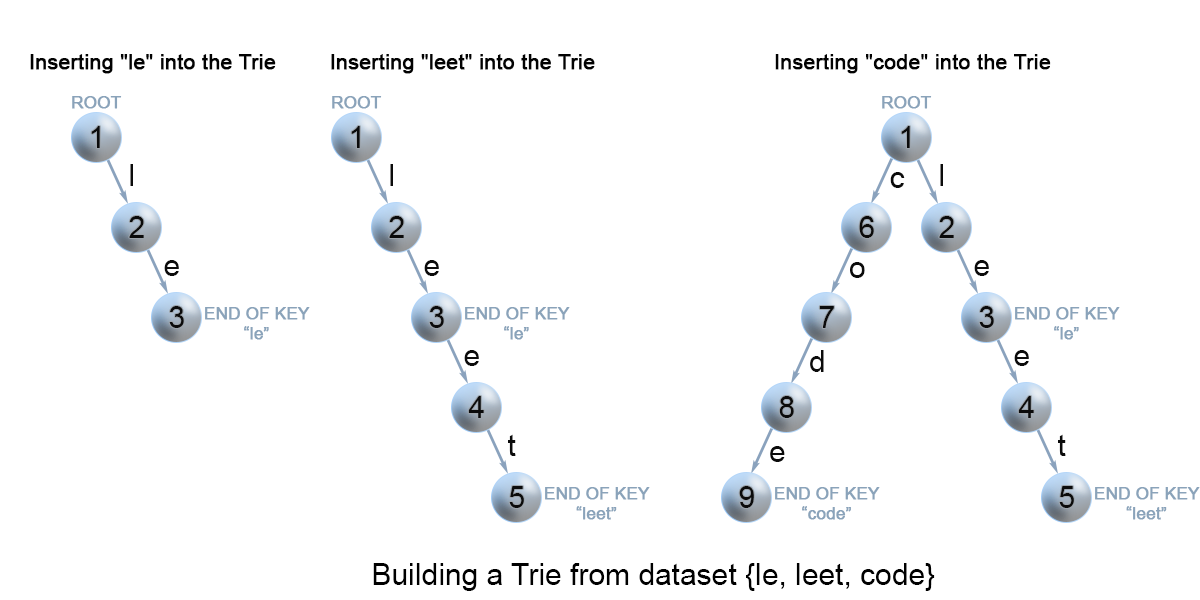
Figure 7. Insertion of keys into a trie.
Java
Complexity Analysis
Time complexity : O(m)O(m), where m is the key length.
In each iteration of the algorithm, we either examine or create a node in the trie till we reach the end of the key. This takes only mm operations.
Space complexity : O(m)O(m).
In the worst case newly inserted key doesn't share a prefix with the the keys already inserted in the trie. We have to add mm new nodes, which takes us O(m)O(m) space.
Search for a key in a trie
Each key is represented in the trie as a path from the root to the internal node or leaf. We start from the root with the first key character. We examine the current node for a link corresponding to the key character. There are two cases :
A link exist. We move to the next node in the path following this link, and proceed searching for the next key character.
A link does not exist. If there are no available key characters and current node is marked as
isEndwe return true. Otherwise there are possible two cases in each of them we return false :There are key characters left, but it is impossible to follow the key path in the trie, and the key is missing.
No key characters left, but current node is not marked as
isEnd. Therefore the search key is only a prefix of another key in the trie.
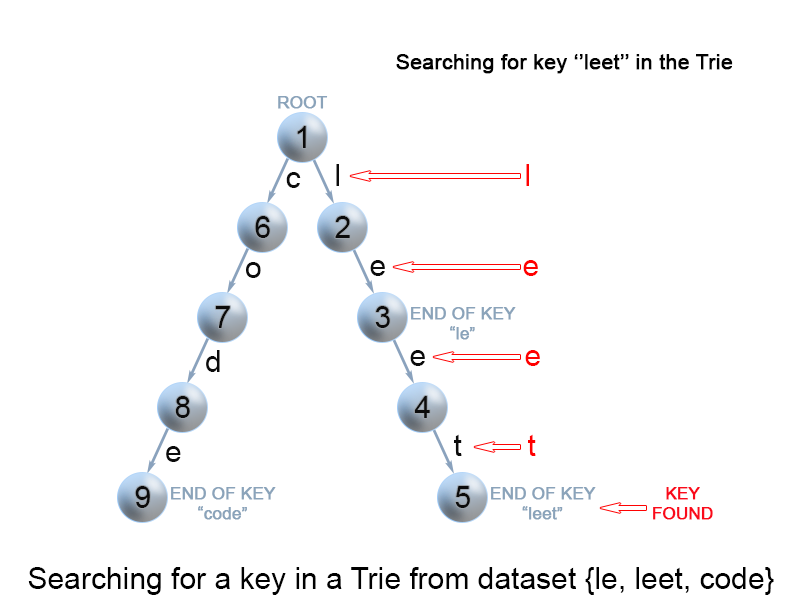
Figure 8. Search for a key in a trie.
Java
Complexity Analysis
Time complexity : O(m)O(m) In each step of the algorithm we search for the next key character. In the worst case the algorithm performs mm operations.
Space complexity : O(1)O(1)
Search for a key prefix in a trie
The approach is very similar to the one we used for searching a key in a trie. We traverse the trie from the root, till there are no characters left in key prefix or it is impossible to continue the path in the trie with the current key character. The only difference with the mentioned above search for a key algorithm is that when we come to an end of the key prefix, we always return true. We don't need to consider the isEnd mark of the current trie node, because we are searching for a prefix of a key, not for a whole key.
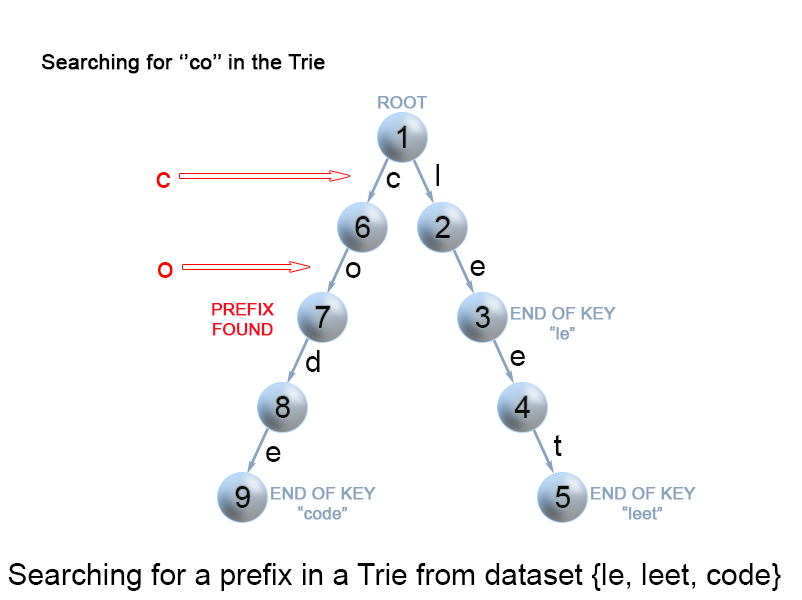
Figure 9. Search for a key prefix in a trie.
Java
Complexity Analysis
Time complexity : O(m)O(m)
Space complexity : O(1)O(1)
Last updated