51.N-Queens (H)
https://leetcode.com/problems/n-queens/
1.Description(Medium)
The n-queens puzzle is the problem of placing n queens on ann×nchessboard such that no two queens attack each other.
Given an integern, return all distinct solutions to the n-queens puzzle.
Each solution contains a distinct board configuration of the n-queens' placement, where'Q'and'.'both indicate a queen and an empty space respectively.
Example
There exist two distinct solutions to the 4-queens puzzle:
[
// Solution 1
[".Q..",
"...Q",
"Q...",
"..Q."
],
// Solution 2
["..Q.",
"Q...",
"...Q",
".Q.."
]
]Can you do it without recursion?
2.Code
https://www.jiuzhang.com/problem/n-queens/
Version 1:
用一个ArrayList<Integer>cols 表示一种方案。表示第i行的皇后放在cols(i) 这个位置上。
DFS+backtracking
dfs(n,cols,result)--n 指的是table size, cols的在第i行的第j个位置放一个皇后,
结束条件:当cols的大小为n时,将cols转换为一个结果。放进result
isValid(cols,column)--指的是当前cols已经有a个值,即在0~a-1行已经放置好了不冲突的皇后,现在在第a行放在column位置一个皇后,但是否与前面所有的皇后冲突。首先不能在同一列中,其次不能再一个对角线上,即他们的row之差和column之差不能相等。
toStringList(cols)--把他转换成一种方案。
题目分析
这个问题要求把n个皇后放在一个nXn的棋盘上,使得任何两个皇后都不能相互攻击,即它们不能同行,不能同列,也不能位于同一条对角线上。对于n=1,问题的解很简单,而且很容易看出对于n=2和n=3来说,这个问题是无解的。所以我们考虑4皇后问题,并用回溯法对它求解。
算法思路
因为每个皇后都必须分别占据一行,我们需要做的不过是棋盘上的每个皇后分配一列。
下面我们用4皇后的求解过程来讲解算法思路:
从空棋盘开始,然后把皇后1 放到它所在行的第-一个可能位置上,也就是第一-行第一列。对于皇后2,在经过第-列和第二列的失败尝试之后,我们把它放在第一个可能的位置,就是格子(2, 3),位于第二行第三列的格子。这被证明是一个死胡同,因为皇后3将没有位置可放。所以,该算法进行回溯,把皇后2放在下一个可能位置(2,4)上。这样皇后3就可以放在(3, 2),这被证明是另一个死胡同。该算法然后就回溯到底,把皇后1移到(1,2)。 接着皇后2到(2,4), 皇后3到(3,1), 而皇后4到(4, 3), 这就是该问题的一个解。
整个过程实际上就是一个状态树的遍历过程
下图为状态树
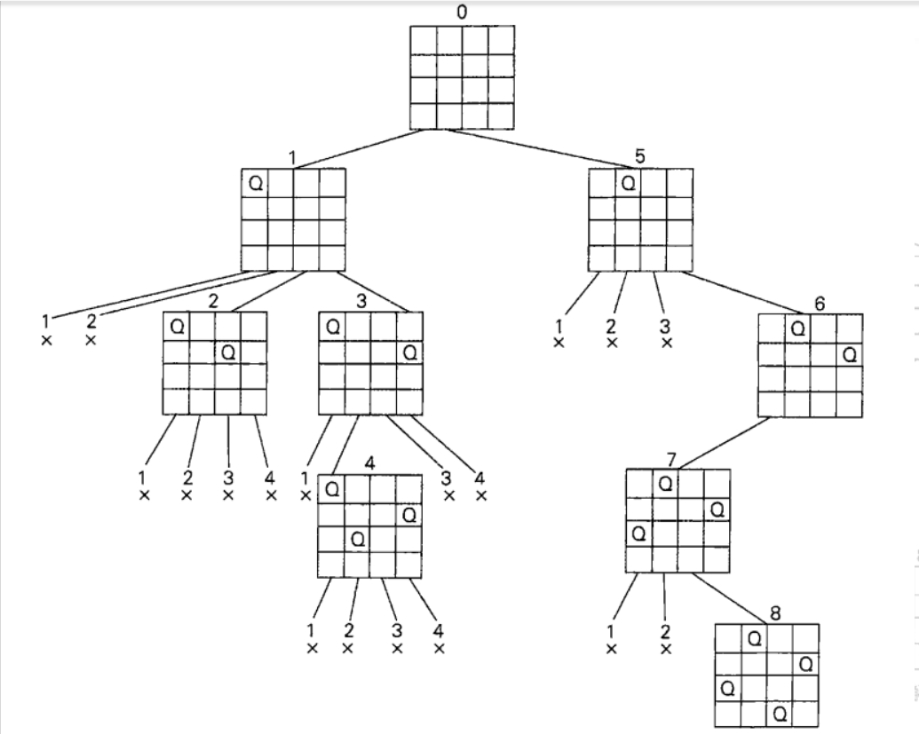
代码思路
按行摆放,在确定一个皇后应该摆的列时,需要检查当前列是否合法,如果合法,则将皇后放置在当前位置,并进行递归,回溯。每行都摆满皇后时,则产生了一种解法,将所有解法收集并返回。
合法性判断方法:当前将要摆放皇后的位置和其他已摆放皇后的位置不能在同一列,且不能在同一条斜线上。这里判断是否在同一条斜线上可以通过两个皇后的位置横坐标之差和纵坐标之差的绝对值是否相等来判断。
复杂度分析
空间复杂度:
O(N!)O(N!)
时间复杂度:
O(N!)O(N!)
放置第一个皇后有 N 种可能,放置两个皇后不超过N(N-2)种可能,放置三个皇后不超过N(N - 2)(N - 4)种可能 ,以此类推。
Version 2:
Video: 回溯算法框架套路详解
这个问题很经典了,简单解释一下:给你一个 N×N 的棋盘,让你放置 N 个皇后,使得它们不能互相攻击。
PS:皇后可以攻击同一行、同一列、左上左下右上右下四个方向的任意单位。
这个问题本质上跟全排列问题差不多,决策树的每一层表示棋盘上的每一行;每个节点可以做出的选择是,在该行的任意一列放置一个皇后。
因为 C++ 代码对字符串的操作方便一些,所以这道题我用 C++ 来写解法,直接套用回溯算法框架:
这部分主要代码,其实跟全排列问题差不多,isValid 函数的实现也很简单:
PS:肯定有读者问,按照 N 皇后问题的描述,我们为什么不检查左下角,右下角和下方的格子,只检查了左上角,右上角和上方的格子呢?
因为皇后是一行一行从上往下放的,所以左下方,右下方和正下方不用检查(还没放皇后);因为一行只会放一个皇后,所以每行不用检查。也就是最后只用检查上面,左上,右上三个方向。
函数 backtrack 依然像个在决策树上游走的指针,通过 row 和 col 就可以表示函数遍历到的位置,通过 isValid 函数可以将不符合条件的情况剪枝:
如果直接给你这么一大段解法代码,可能是懵逼的。但是现在明白了回溯算法的框架套路,还有啥难理解的呢?无非是改改做选择的方式,排除不合法选择的方式而已,只要框架存于心,你面对的只剩下小问题了。
当 N = 8 时,就是八皇后问题,数学大佬高斯穷尽一生都没有数清楚八皇后问题到底有几种可能的放置方法,但是我们的算法只需要一秒就可以算出来所有可能的结果。
不过真的不怪高斯。这个问题的复杂度确实非常高,看看我们的决策树,虽然有 isValid 函数剪枝,但是最坏时间复杂度仍然是 O(N^(N+1)),而且无法优化。如果 N = 10 的时候,计算就已经很耗时了。
有的时候,我们并不想得到所有合法的答案,只想要一个答案,怎么办呢?比如解数独的算法,找所有解法复杂度太高,只要找到一种解法就可以。
其实特别简单,只要稍微修改一下回溯算法的代码即可:
这样修改后,只要找到一个答案,for 循环的后续递归穷举都会被阻断。也许你可以在 N 皇后问题的代码框架上,稍加修改,写一个解数独的算法?
Last updated